Human iPSC model reveals a central role for NOX4 and oxidative stress in Duchenne cardiomyopathy
Robin Duelen, Domiziana Costamagna, Guillaume Gilbert, Liesbeth De Waele, Nathalie Goemans, Kaat Desloovere, Catherine M Verfaillie, Karin R Sipido, Gunnar M Buyse, Maurilio Sampaolesi
Abstract
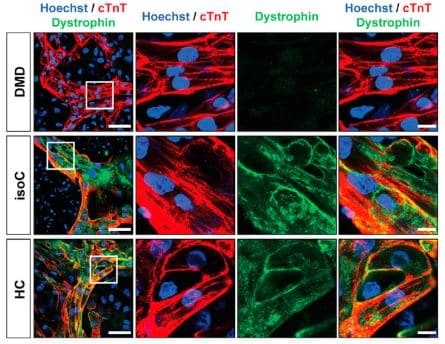
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a progressive muscle disorder caused by mutations in the Dystrophin gene. Cardiomyopathy is a major cause of early death. We used DMD-patient-specific human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) to model cardiomyopathic features and unravel novel pathologic insights. Cardiomyocytes (CMs) differentiated from DMD hiPSCs showed enhanced premature cell death due to significantly elevated intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) resulting from depolarized mitochondria and increased NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4). CRISPR-Cas9 correction of Dystrophin restored normal ROS levels. ROS reduction by N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), ataluren (PTC124), and idebenone improved hiPSC-CM survival. We show that oxidative stress in DMD hiPSC-CMs was counteracted by stimulating adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production. ATP can bind to NOX4 and partially inhibit the ROS production. Considering the complexity and the early cellular stress responses in DMD cardiomyopathy, we propose targeting ROS production and preventing detrimental effects of NOX4 on DMD CMs as promising therapeutic strategy.